ECSC 2019 - The Pytector
13 May 2019description: Retrouver le numéro de série pour valider le challenge
category: reverse - 484
A zip file is attached to the description.
The zip file contains a .exe and some .pyd (dll) files.
Looking to IDA strings, I found some interesting things:
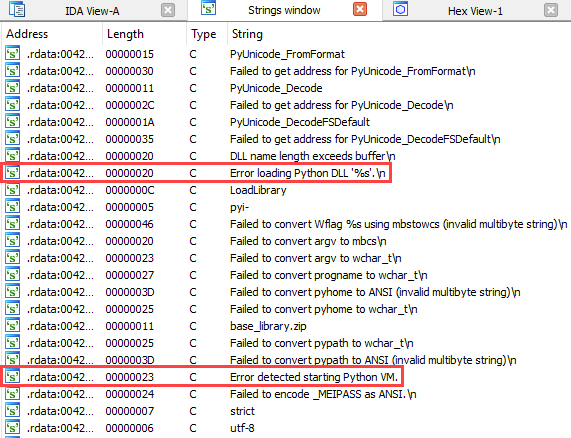
Also, I found interesting things with strings:
# strings check_serial.exe | grep check
incorrect header check
incorrect data check
incorrect length check
sfake_check <---- interestingWith these information, we can guess some python scripts are packed in the PE and executed in a VM with python37.dll
I found a tool on github to extract these files:
# ls -l
total 1188
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1513 May 15 20:32 fake_check
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4171 May 15 20:32 pyiboot01_bootstrap
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1838 May 15 20:32 pyimod01_os_path
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 9381 May 15 20:32 pyimod02_archive
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 18701 May 15 20:32 pyimod03_importers
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1161295 May 15 20:32 PYZ-00.pyz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 357 May 15 20:32 structIt is PYC file but the header is missing, I tried some tools but it didnt work well, then I found an online decompiler.
This is the fake_check.py file:
passwd = [
432, 360, 264, 184, 56, 344, 340, 268, 280, 172, 64, 300, 320, 356, 356, 296, 328, 504, 356, 276, -4, 348, 52, 304, 256, 264, 184, 48, 280, 344, 312, 168, 296, -4, 128, 256, 264, 184, 40, 296, 340, 52, 280, 80, 504, 300, 296]
p = [43, 8, 26, 11, 3, 1, 46, 10, 28, 23, 13, 33, 0, 45, 34, 37, 16, 5, 36, 32, 9, 4, 20, 19, 25, 22, 17, 7, 27, 14, 42, 41, 18, 2, 6, 40, 30, 29, 15, 21, 44, 24, 39, 12, 35, 38, 31]
def check(serial):
global p
global passwd
serialsize = len(serial)
key = 'Complex is better than complicated'
result = []
for i in range(serialsize):
result.append(((serial[p[i]] ^ key[(i % len(key))]) << 2) - 4)
return result == passwd
def successful(serial):
print('Good job!\nECSC}'.format(serial.decode('utf-8')))
def defeated():
print('Not really')
def main():
import pytector
serial = input('Serial number: ').encode('utf-8')
if check(serial):
successful(serial)
else:
defeated()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()I don’t know why but the script it XORing 2 char and it throws an error… I patched it adding the ord function, but I actually don’t know how it is working in…
Okay the check function is easy to bruteforce (and we can guess the flag length: 47):
import string
passwd = [432, 360, 264, 184, 56, 344, 340, 268, 280, 172, 64, 300, 320, 356, 356, 296, 328, 504, 356, 276, -4, 348, 52, 304, 256, 264, 184, 48, 280, 344, 312, 168, 296, -4, 128, 256, 264, 184, 40, 296, 340, 52, 280, 80, 504, 300, 296]
p = [43, 8, 26, 11, 3, 1, 46, 10, 28, 23, 13, 33, 0, 45, 34, 37, 16, 5, 36, 32, 9, 4, 20, 19, 25, 22, 17, 7, 27, 14, 42, 41, 18, 2, 6, 40, 30, 29, 15, 21, 44, 24, 39, 12, 35, 38, 31]
def uncheck(serial, i):
global p
global passwd
serialsize = len(serial)
key = 'Complex is better than complicated'
result = (( ord(serial[p[i]]) ^ ord(key[(i % len(key))])) << 2) - 4
return result == passwd[i]
def bruteforce_check():
global p
global passwd
result = "?"*47
for i in range(47):
for j in string.printable:
tmp = list(result)
tmp[p[i]] = j
result = ''.join(tmp)
if uncheck(result, i):
break
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
serial = bruteforce_check()
print(serial)This is our output:
42dc6_ba4ad_f14g!_....._....._....._....._.....Well it seems that this is not the correct flag.
Looking closely to the fake_check.py code, we forgot the import pytector line…
Okay let’s see the pytector.pyd (in the initial .zip).
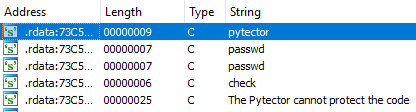
This strings lead us to some code modifying the fake_check during its execution.
The passwd table is modified:

The p table is modified:
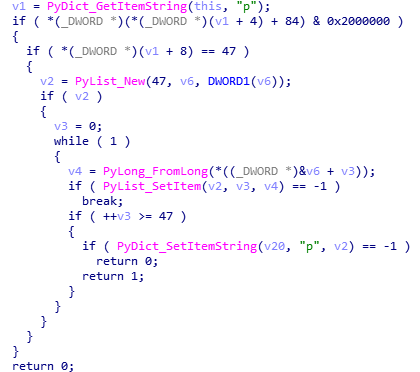
And the check function bytecodes is modified too:

It is possible to do it in static but I prefer the dynamic way.
You cannot modify the check function (for example add some print) because the pytector will detect it and won’t work.
I added the pdb module to debug the script:
passwd = [
432, 360, 264, 184, 56, 344, 340, 268, 280, 172, 64, 300, 320, 356, 356, 296, 328, 504, 356, 276, -4, 348, 52, 304, 256, 264, 184, 48, 280, 344, 312, 168, 296, -4, 128, 256, 264, 184, 40, 296, 340, 52, 280, 80, 504, 300, 296]
p = [43, 8, 26, 11, 3, 1, 46, 10, 28, 23, 13, 33, 0, 45, 34, 37, 16, 5, 36, 32, 9, 4, 20, 19, 25, 22, 17, 7, 27, 14, 42, 41, 18, 2, 6, 40, 30, 29, 15, 21, 44, 24, 39, 12, 35, 38, 31]
def check(serial):
global p
global passwd
serialsize = len(serial)
key = 'Complex is better than complicated'
result = []
for i in range(serialsize):
result.append(((serial[p[i]] ^ key[(i % len(key))]) << 2) - 4)
return result == passwd
def successful(serial):
print('Good job!\nECSC}'.format(serial.decode('utf-8')))
def defeated():
print('Not really')
def main():
import pytector
import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
serial = "b"*47
if check(serial):
successful(serial)
else:
defeated()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()This is what I’ve done in the debugger:
# python fake_check.py
> c:\users\ieuser\desktop\new\dist\fake_check.py(26)main()
-> serial = "b"*47
(Pdb) print(p)
[12, 36, 23, 17, 27, 34, 18, 25, 33, 42, 22, 21, 45, 20, 35, 13, 30, 38, 31, 28, 26, 10, 44, 29, 9, 11, 2, 4, 14, 1, 37, 15, 41, 19, 39, 24, 6, 7, 46, 32, 5, 8, 0, 3, 16, 43, 40]
(Pdb) print(passwd)
[1147, 1778, 1721, 1929, 1821, 1680, 2064, 654, 1822, 1842, 651, 1602, 1627, 1952, 1865, 1629, 1899, 608, 1951, 1755, 1610, 1711, 611, 1689, 1774, 1721, 1931, 1823, 1739, 1582, 1619, 1954, 1593, 1693, 1149, 1772, 1802, 1932, 1739, 1680, 2057, 604, 1824, 1834, 608, 1598, 1628]
(Pdb) print(check.__code__.co_varnames)
('serial', 'serialsize', 'key', 'result', 'i')
(Pdb) print(check.__code__.co_consts)
(None, 'Complex is better than complicated', 4, 42)
(Pdb) print(check.__code__.co_names)
('len', 'range', 'append', 'p', 'passwd')
(Pdb) print(check.__code__.co_code)
b't\x00|\x00\x83\x01}\x01d\x01}\x02g\x00}\x03x:t\x01|\x01\x83\x01D\x00].}\x04|\x03\xa0\x02|\x00t\x03|\x04\x19\x00\x19\x00|\x02|\x04t\x00|\x02\x83\x01\x16\x00\x19\x00d\x02>\x00A\x00d\x03\x17\x00\xa1\x01\x01\x00q\x1aW\x00|\x03t\x04k\x02S\x00'Okay we have everything we need. Using the dis module we can disassemble the co_code:
>>> import dis
>>> a = b't\x00|\x00\x83\x01}\x01d\x01}\x02g\x00}\x03x:t\x01|\x01\x83\x01D\x00].}\x04|\x03\xa0\x02|\x00t\x03|\x04\x19\x00\x19\x00|\x02|\x04t\x00|\x02\x83\x01\x16\x00\x19\x00d\x02>\x00A\x00d\x03\x17\x00\xa1\x01\x01\x00q\x1aW\x00|\x03t\x04k\x02S\x00'
>>> dis.dis(a)
0 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (0)
2 LOAD_FAST 0 (0)
4 CALL_FUNCTION 1
6 STORE_FAST 1 (1)
8 LOAD_CONST 1 (1)
10 STORE_FAST 2 (2)
12 BUILD_LIST 0
14 STORE_FAST 3 (3)
16 SETUP_LOOP 58 (to 76)
18 LOAD_GLOBAL 1 (1)
20 LOAD_FAST 1 (1)
22 CALL_FUNCTION 1
24 GET_ITER
>> 26 FOR_ITER 46 (to 74)
28 STORE_FAST 4 (4)
30 LOAD_FAST 3 (3)
32 LOAD_METHOD 2 (2)
34 LOAD_FAST 0 (0)
36 LOAD_GLOBAL 3 (3)
38 LOAD_FAST 4 (4)
40 BINARY_SUBSCR
42 BINARY_SUBSCR
44 LOAD_FAST 2 (2)
46 LOAD_FAST 4 (4)
48 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (0)
50 LOAD_FAST 2 (2)
52 CALL_FUNCTION 1
54 BINARY_MODULO
56 BINARY_SUBSCR
58 LOAD_CONST 2 (2)
60 BINARY_LSHIFT
62 BINARY_XOR
64 LOAD_CONST 3 (3)
66 BINARY_ADD
68 CALL_METHOD 1
70 POP_TOP
72 JUMP_ABSOLUTE 26
>> 74 POP_BLOCK
>> 76 LOAD_FAST 3 (3)
78 LOAD_GLOBAL 4 (4)
80 COMPARE_OP 2 (==)
82 RETURN_VALUENice, all we have to do is to read this.
I added comments to understand it:
(PS:
LOAD_CONST index -> load co_consts[index]
LOAD_GLOBAL index -> load co_names[index]
LOAD_FAST index -> load co_varnames[index])
0 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (0) # load len
2 LOAD_FAST 0 (0) # load serial
4 CALL_FUNCTION 1 # call len(serial)
6 STORE_FAST 1 (1) # serialsize = len(serial)
8 LOAD_CONST 1 (1) # load 'Complex is better than complicated'
10 STORE_FAST 2 (2) # key = 'Complex is better than complicated'
12 BUILD_LIST 0 # []
14 STORE_FAST 3 (3) # result = []
16 SETUP_LOOP 58 (to 76)
18 LOAD_GLOBAL 1 (1) # range
20 LOAD_FAST 1 (1) # serialsize
22 CALL_FUNCTION 1 # call range
24 GET_ITER
>> 26 FOR_ITER 46 (to 74) # start for
28 STORE_FAST 4 (4) # i
30 LOAD_FAST 3 (3) # result
32 LOAD_METHOD 2 (2) # result.append()
34 LOAD_FAST 0 (0) # serial
36 LOAD_GLOBAL 3 (3) # serial[p]
38 LOAD_FAST 4 (4) # sesrial[p[i]]
40 BINARY_SUBSCR # serial[p[i]]
42 BINARY_SUBSCR # serial[p[i]]
44 LOAD_FAST 2 (2) # key
46 LOAD_FAST 4 (4) # key[i]
48 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (0) # len
50 LOAD_FAST 2 (2) # key[i % len(key)]
52 CALL_FUNCTION 1 # key[i % len(serialsize)]
54 BINARY_MODULO # key[i % len(serialsize)]
56 BINARY_SUBSCR # key[i % len(serialsize)]
58 LOAD_CONST 2 (2) # key[i % len(serialsize)] << 4
60 BINARY_LSHIFT
62 BINARY_XOR # (serial[p[i]] ^ key[i % len(serialsize)] << 4)
64 LOAD_CONST 3 (3) # 42
66 BINARY_ADD # (serial[p[i]] ^ key[i % len(serialsize)] << 4) + 42
68 CALL_METHOD 1
70 POP_TOP
72 JUMP_ABSOLUTE 26
>> 74 POP_BLOCK # Same than original file
>> 76 LOAD_FAST 3 (3)
78 LOAD_GLOBAL 4 (4)
80 COMPARE_OP 2 (==)
82 RETURN_VALUEOkay we have the new code, we can finaly get the flag:
import string
p = [12, 36, 23, 17, 27, 34, 18, 25, 33, 42, 22, 21, 45, 20, 35, 13, 30, 38, 31, 28, 26, 10, 44, 29, 9, 11, 2, 4, 14, 1, 37, 15, 41, 19, 39, 24, 6, 7, 46, 32, 5, 8, 0, 3, 16, 43, 40]
passwd = [1147, 1778, 1721, 1929, 1821, 1680, 2064, 654, 1822, 1842, 651, 1602, 1627, 1952, 1865, 1629, 1899, 608, 1951, 1755, 1610, 1711, 611, 1689, 1774, 1721, 1931, 1823, 1739, 1582, 1619, 1954, 1593, 1693, 1149, 1772, 1802, 1932, 1739, 1680, 2057, 604, 1824, 1834, 608, 1598, 1628]
def uncheck(serial, i):
global p
global passwd
serialsize = len(serial)
key = 'Complex is better than complicated'
result = (ord(serial[p[i]]) ^ (ord(key[(i % len(key))]) << 4))+ 42
return result == passwd[i]
def bruteforce_check():
global p
global passwd
result = "?"*47
for i in range(47):
for j in string.printable:
tmp = list(result)
tmp[p[i]] = j
result = ''.join(tmp)
if uncheck(result, i):
break
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
serial = bruteforce_check()
print(serial)And the output:
# python final.py
f4a05_0b24e_ac186_f368a_2d031_a56d6_896cb_849aaThis is the good flag: ECSC{f4a05_0b24e_ac186_f368a_2d031_a56d6_896cb_849aa}
